Advancing a career in IT can be challenging, especially because the industry never stands still. Staying ahead means actively pursuing personal and professional growth while embracing new opportunities. So, what steps can those currently in IT positions take to have a successful career development journey in IT?
This guide provides a clear roadmap with practical tips and real-world examples of senior IT jobs current employees can pursue.
Table of Contents
- The Importance of Climbing the Ladder
- 8 IT Career Development Tips
- Skills Needed for Senior IT Roles
- Examples of Senior IT Jobs
- Browse Open IT Positions
The Importance of Climbing the Ladder
Career development in IT involves more than increasing a salary or gaining a new title. It requires staying competitive and relevant in an ever-changing field. As technology continues to advance, the demand for higher-level skills grows. Climbing the ladder ensures professionals keep pace with industry changes while positioning themselves for leadership roles in the future.
Career development in the IT industry opens doors to more varied and challenging projects. It offers the chance to specialize in one’s areas of interest or explore new technologies. These new opportunities can also lead to a broader influence within an organization. It can allow professionals to start shaping decisions, innovating and driving business success.
Career progression also brings a sense of accomplishment and personal growth. It creates a path for people to refine their expertise and build strong professional networks. It offers a personal and professional value increase. IT employees can also avoid career stagnation and maintain long-term job satisfaction by seeking out new challenges.
8 IT Career Development Tips
Advancing a career can bring long-term benefits to one’s professional journey, and IT professionals can implement various strategies to grow in their careers. While it may take time and consistency to reap the benefits of one’s hard work, it will be worth it when it results in a promotion. To begin driving innovation and realizing life’s potential, employees can start with these eight IT career development tips.
1. Keep Learning
Existing IT employees may have already completed a certificate or degree in their respective field to attain a job. However, one never stops learning — and an advanced career requires advanced knowledge and skills. Ongoing learning plays a key role in career development because the IT field constantly evolves.
Depending on the individual and the specific IT leadership position they want to achieve, various opportunities exist for continued learning. Methods of developing in-demand skills include:
- Completing courses and certifications: Accredited online certifications and courses provide perfect opportunities to fill any skill gaps.
- Attending workshops and conferences: Because the IT industry constantly changes, employees can search and attend these events to stay updated on the latest trends and best practices.
- Reading industry publications: Reading industry publications can help one stay informed about the latest industry news. Examples of such online publications include Network World, TechRepublic and ZDNET.
- Participating in community forums: Employees can participate in community forums and groups to learn about real-life IT problems and solutions. Community platforms include LinkedIn, Reddit and other specialized forums.
- Consulting mentors and peers: Sometimes, the best way to learn involves receiving constructive criticism from a mentor or peers.

2. Escape the Comfort Zone
Staying in a comfort zone may feel safe, but it can lead to stagnation in IT careers. The fast pace of technological change means that remaining comfortable often equates to falling behind. One must recognize when work becomes routine and easy. Easy work might signal mastery, but it can also be a warning sign of complacency.
To break free, employees should focus on their personal growth with questions like:
- Am I seeking out challenging projects, or do I stick to what’s familiar?
- When was the last time I learned a new technology or skill?
- Am I taking advantage of mentorship or networking opportunities to gain new perspectives?
- Do I regularly seek feedback on my work to identify areas for improvement?
- Am I keeping up with industry trends or relying on outdated knowledge?
Answering these questions helps to avoid complacency and fuels continuous development, helping one to stretch outside their comfort zone.
3. Find a Mentor
Everyone in a company plays a role — from associates to management. Each department, team and position has a specific set of responsibilities that help the business operate and achieve its goals. Thus, to advance in a leadership role, one must learn the expectations for such a position — and to do that, one must find a mentor.
A mentor can be anybody inside or outside the company — be it a manager, colleague, friend or family member. These trusted and admired individuals provide a source of inspiration and expertise. The ideal mentor understands an employee’s professional goals.
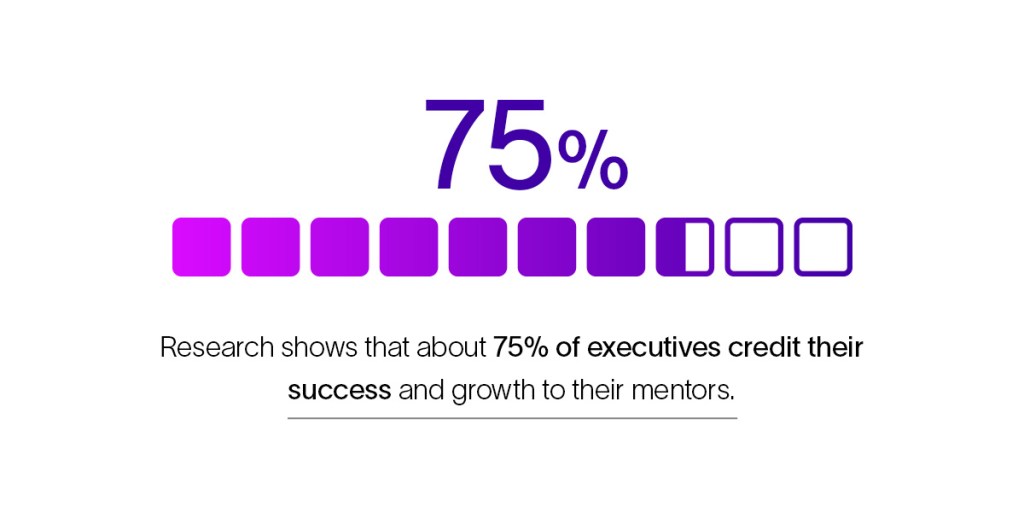
Research shows that about 75% of executives credit their success and growth to their mentors, and 90% of employees feel satisfied with their careers when they have a career mentor. Mentors provide the guidance, support, advice and feedback that employees need as they grow in their professional lives.
4. Implement an IT Career Development Plan
A structured career development plan can make all the difference in one’s professional journey. Without a clear roadmap, it’s easy to lose focus or miss out on valuable growth opportunities. Creating and following a personalized plan ensures that employees set goals, track their progress and develop their skills.

IT professionals can start by outlining short-term and long-term goals. These objectives could include anything and should be customized to their progression path. Examples include gaining certifications, learning specific tools and technologies, or transitioning into leadership roles. After identifying their goals, employees must identify the skills or knowledge gaps needed to reach them and actively work on filling those gaps.
With implementation comes evaluation. IT professionals should regularly revisit and adjust the plan as their industry or company evolves. Staying adaptable helps one remain relevant and prepared for new opportunities.
5. Accept Feedback
With any career — and especially with a mentor — comes feedback. To become a leader, one must learn to accept input and turn it into a growth opportunity. Receiving constructive feedback can be challenging, but it’s an exceptional skill to develop in the workplace.
To become more accepting of feedback, employees can:
- Ask for feedback often.
- Keep an open and positive mindset.
- Listen to understand and not to respond.
- Connect feedback to the role and not themselves.
- Remember that feedback offers the opportunity to improve.
- Feel free to ask any questions without challenging the feedback given.
6. Take the Lead
IT employees must challenge themselves and jump into the deep end. Sometimes, taking the lead may be the best way to learn and grow into a senior position. Aspiring IT seniors must be on the lookout for potential opportunities to lead small projects or even mentor new or junior staff. These opportunities present the perfect chance to develop one’s leadership and management skills.
Sometimes, these moments may emerge unexpectedly, and employees will have to put their fear aside to volunteer to take charge and take responsibility. For instance, the time may come when a team leader takes a weeks-long leave of absence or leaves the company permanently. Employees looking to grow can show their eagerness to accept more responsibility while the company adjusts.
7. Bring Value
Employees get paid for the value they bring to a company. To become an asset to an employer, those who want to advance their IT career must try to be more than an overhead cost. These employees must aim to make the work they do measurable, actual and beneficial.

Employees can increase their worth by increasing revenue, decreasing costs or looking beyond the bottom line. Having a positive, tangible or measurable impact on a business can help employees stand out from the crowd and gain the attention of higher-ups. Growth-minded team members keep the bigger picture in mind — helping the company and its clients.
8. Capitalize on Characteristics
Employers value various skills and characteristics when hiring for IT positions. Hard and technical skills, such as coding and database management, make up most of an IT employee’s responsibilities. Staff must also master soft skills, such as communication and creativity, that allow them to work well with other people.
Certain traits and skills help individuals grow and thrive in leadership roles. These characteristics include:
- Collaboration: Some personalities work better with or without people. However, being a leader means collaborating effectively with other people, teams or departments.
- Initiative: Those who want to become leaders must be able to take initiative. This trait can be a big indicator for employers, helping them gauge an employee’s abilities to help a team and keep everyone moving forward.
- Continuous learning: Those who want to advance in their career must also advance their learning and skills. Stay updated on new trends, technologies, processes and frameworks to improve and stand out.
- Passion: With passion comes drive, discipline and dedication. Those who have a passion for what they do can be a source of motivation and inspiration for team members. Passion also helps drive individuals to learn and grow.
- Critical thinking: Employees often approach leaders with problems. Valuable skills include asking the right questions, filling in the gaps and making wise decisions.
- Prediction: Leaders look forward to where employees will need them, where the company will head and how the market will change. Cultivating their intuitiveness can also give leaders the confidence to take initiative.
- Curiosity: Having an open mind and a curiosity to know more helps one learn new things on a deeper level. A natural curiosity helps one learn continuously.
- Self-motivation: Passion, curiosity and dedication all come together to help fuel one’s self-motivation. And motivation is infectious, prompting teams to work toward a common goal.
Current IT employees who have these traits must capitalize on them, whereas those who don’t must learn to adapt and grow in them. Employers typically seek these characteristics in leadership roles.
In addition to these strategies, employees can explore various other tips for advancing a career, regardless of the industry. Employees must assess their present position, where they want to be and how they want to achieve these goals.
Must-Have Skills for Senior IT Roles
Advancing to senior IT job titles requires a diversified skill set that goes beyond technical expertise. Senior IT professionals must combine their technical knowledge with leadership, strategic thinking and effective communication to drive innovation and solve complex problems.
Employees need these essential skills to excel at this level.
Technical Mastery
At the senior level, a deep understanding of core technologies is a must. Employees might cultivate expertise in cloud computing, cybersecurity, networking, software development and more, depending on the specific IT job category. Experience in the latest tools and platforms relevant to the organization is also a necessity. Senior IT professionals should also be able to integrate and implement new technologies as effectively as possible to ensure their company’s systems remain efficient and secure.
Leadership and Mentorship
Leadership skills play an essential role in senior IT jobs. These professionals often oversee teams, help guide them through projects and mentor junior co-workers. The ability to inspire and motivate others assures that the entire team thrives. Strong leadership also means making tough decisions and resolving conflicts while focusing on team and business goals.
Strategic Thinking
IT leaders must be able to think beyond day-to-day operations. They use their strategic thinking skills to understand how technology aligns with the company’s broader objectives and how to use IT resources to achieve those goals. Senior professionals should also be able to plan for the long term, assess risks and make informed decisions that support innovation and stability.
Project Management
Another must-have skill involves managing complex projects from conception to execution. The senior IT staff assumes the responsibility for overseeing multiple projects, completing projects by the deadline and allocating resources. They will need to be well-versed in everything from budgeting and scheduling to risk assessment and troubleshooting. Having a strong grasp of project management methodologies like Agile or DevOps is highly beneficial.
Communication Skills
Senior IT roles require clear and effective communication within technical teams and with nontechnical stakeholders. Those seeking higher roles need to become confident with translating complex technical concepts into understandable language for leadership and business partners. Great communication skills ensure that everyone feels aligned on goals and priorities.

Problem-Solving and Adaptability
Senior IT professionals solve complex problems quickly. They identify the root causes of issues and provide scalable solutions. They must also display adaptability skills, staying current with emerging technologies and pivoting when necessary to meet evolving business needs.
Examples of Senior IT Jobs
Various senior IT job titles exist on the market, spanning several specialties. Understanding the responsibilities of each will help guide those interested in advancing their careers. This list of senior IT jobs categorizes them based on their specialty.
Servers, Architecture and Networking
These roles focus on optimizing a business’s IT infrastructure and network systems:
- Senior network engineers: This role requires one to design and manage complex network systems. Senior network engineers oversee the network’s performance, security and reliability. They also handle tasks like troubleshooting and configuring routers and switches.
- IT architects: IT architects focus on designing and managing the overall structure of IT systems, ensuring they align with business goals. They create blueprints for IT systems, integrating hardware, software and networking components.
Cybersecurity and Analytics
Positions dedicated to protecting data and analyzing information include:
- Senior cybersecurity engineers: A key position for safeguarding company assets, this role involves developing and implementing security protocols and measures. A senior cybersecurity engineer assesses any vulnerabilities and responds to security incidents. They typically work to protect sensitive data from breaches.
- Senior data analysts: Senior data analysts work with large datasets to provide insights and help with decision-making. They use advanced analytical tools and techniques to identify trends, patterns and even anomalies.
Cloud Computing

These careers leverage cloud technologies to build scalable and secure IT solutions:
- Senior cloud engineers: This role focuses on various responsibilities regarding cloud-based infrastructure. Senior cloud engineers work with platforms like AWS, Azure or Google Cloud to optimize the business’s cloud performance and security.
- Cloud solutions architects: Responsible for creating cloud strategies and solutions, cloud solutions architects design cloud infrastructures that meet business needs. While designing, they must consider factors like scalability, security and cost-efficiency.
Development and Coding
Professionals can create and advance software applications and platforms to meet business needs with these senior IT job examples:
- Senior software engineers: A senior software engineer leads the development of software applications. They stay involved in all stages of software development, from designing and coding to testing and deployment. They also often mentor junior developers.
- Senior developers: These developers customize and extend software applications to meet their business’s needs. They work on creating custom solutions, integrating one platform with other systems.
Database

These positions assume the responsibility for managing and optimizing databases:
- Senior database administrators (DBAs): Senior DBAs help manage and maintain database systems. They ensure that a database performs well and remains secure. They also handle tasks such as database design, optimization, backup and recovery, and they troubleshoot issues to maintain data integrity.
- Senior data engineers: Data engineers build and maintain data pipelines and databases. They focus on designing data architectures that support analytics and business intelligence.
Project Management
Employees can oversee and coordinate IT projects to deliver successful outcomes with the following positions:
- IT project managers (PMs): The role of an IT PM involves overseeing the planning, execution and completion of numerous IT projects. This position requires budgeting, scheduling, risk management and team coordination skills. The senior IT project manager job description typically includes managing large-scale projects and ensuring their delivery on time and within scope.
- Senior IT business analysts: A senior IT analyst job description mainly revolves around bridging the gap between IT and business. They analyze business needs, gather requirements and propose solutions that align with organizational goals. This role involves extensive collaboration with stakeholders and often includes creating detailed documentation and process improvements.
Help Desk and Customer Support
Individuals can provide advanced technical support as a senior IT support engineer. These positions typically handle advanced technical issues and provide high-level support to users. They often mentor junior support staff and develop troubleshooting procedures. The senior IT support engineer job includes managing escalations and ensuring prompt resolution of complex problems.
Find a Rewarding Future in IT With Danaher
At Danaher, you have the chance to join a global leader in life sciences and diagnostics. We’re dedicated to solving some of the world’s most pressing health challenges, and our IT team plays an integral role in supporting groundbreaking research and advancing technologies that improve lives. By joining Danaher, you’ll contribute to innovative projects that shape the future of health and technology.
If you’re passionate about making a tangible impact and growing within a forward-thinking company, explore IT opportunities at Danaher and help drive advancements that lead to a healthier tomorrow.


Comments
One response to “How to Advance an IT Career”
[…] new hires to show them the ropes and integrate them into the company culture. Research shows that nine in 10 employees with a career mentor are happy with their jobs. If you do not have time to do so, consider […]